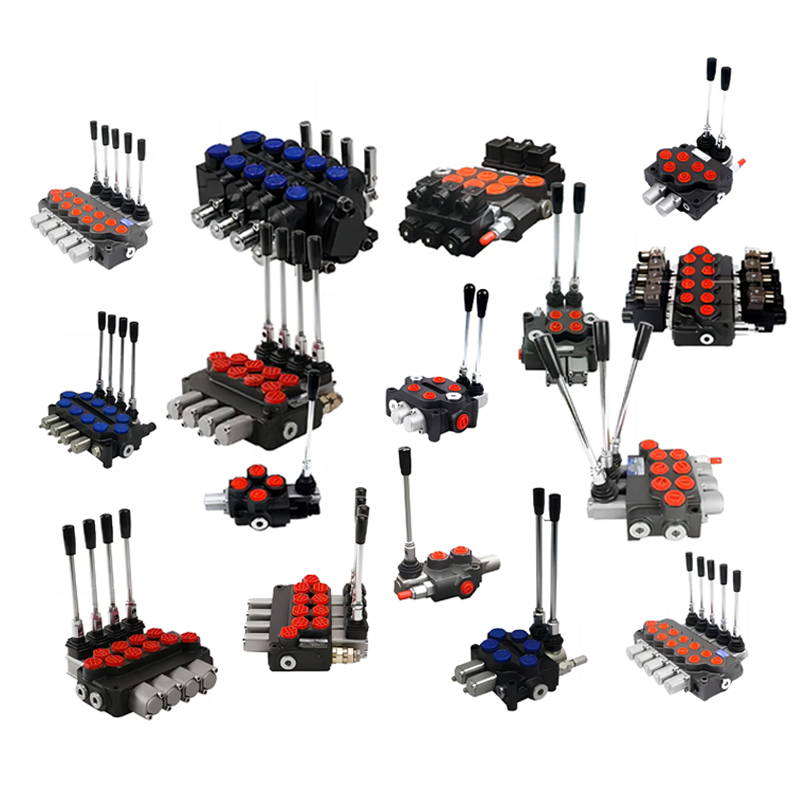
Hydraulic valve is an automatic component operated by pressure oil, which is controlled by the pressure oil of the pressure distribution valve. It is usually used in combination with electromagnetic pressure distribution valves, and can be used to remotely control the on-off of oil, gas, and water pipeline systems in hydropower stations. Commonly used in oil circuits such as clamping, control, and lubrication. There are direct acting type and pilot type, and the pilot type is commonly used.
Classification:
Classification by control method: manual, electronic, hydraulic
Classification by function: flow valve (throttle valve, speed regulating valve, shunt and collector valve), pressure valve (overflow valve, pressure reducing valve, sequence valve, unloading valve), directional valve (electromagnetic directional valve, manual directional valve, one-way valve, hydraulic control one-way valve)
Classified by installation method: plate valve, tubular valve, superposition valve, threaded cartridge valve, cover plate valve
According to the operation mode, it is divided into manual valve, motorized valve, electric valve, hydraulic valve, electro-hydraulic valve, etc.
Pressure control:
It is divided into overflow valve, pressure reducing valve, and sequence valve according to its purpose. ⑴ Relief valve: can control the hydraulic system to maintain a constant state when reaching the set pressure. The overflow valve used for overload protection is called a safety valve. When the system fails and the pressure rises to a limit that may cause damage, the valve port will open and overflow to ensure the safety of the system Pressure reducing valve: It can control the branch circuit to obtain a stable pressure lower than the main circuit oil pressure. According to the different pressure functions it controls, pressure reducing valves can also be divided into fixed value pressure reducing valves (output pressure is a constant value), constant differential pressure reducing valves (input and output pressure difference is a constant value), and constant ratio pressure reducing valves (input and output pressure maintain a certain proportion) Sequence valve: It can make one actuating element (such as hydraulic cylinder, hydraulic motor, etc.) act, and then make other actuating elements act in sequence. The pressure generated by the oil pump first pushes the hydraulic cylinder 1 to move, while acting on the area A through the oil inlet of the sequence valve. When the movement of the hydraulic cylinder 1 is complete, the pressure rises. After the upward thrust acting on the area A is greater than the set value of the spring, the valve core rises to connect the oil inlet and outlet, causing the hydraulic cylinder 2 to move
Flow control:
The throttle area between the valve core and valve body and the local resistance generated by it are used to adjust the flow rate, thereby controlling the movement speed of the actuator. Flow control valves are divided into 5 types according to their purpose. ⑴ Throttle valve: After adjusting the throttle area, the movement speed of actuator components that have little change in load pressure and low requirements for motion uniformity can be basically stable Speed regulating valve: It can maintain the inlet and outlet pressure difference of the throttle valve as a constant value when the load pressure changes. In this way, after the throttle area is adjusted, regardless of the change in load pressure, the speed regulating valve can maintain the flow rate through the throttle valve unchanged, thereby stabilizing the movement speed of the actuator Diverter valve: An equal flow diverter valve or synchronizing valve that enables two actuating elements of the same oil source to achieve equal flow regardless of load; The proportional flow divider valve is obtained by distributing the flow in proportion Collecting valve: Its function is opposite to that of the diverter valve, which distributes the flow into the collecting valve in proportion Diverter and collector valve: It has two functions: a diverter valve and a collector valve.
requirement:
1) Flexible action, reliable function, low impact and vibration during operation, low noise, and long service life.
2) When the fluid passes through the hydraulic valve, the pressure loss is small; When the valve port is closed, it has good sealing performance, small internal leakage, and no external leakage.
3) The controlled parameters (pressure or flow) are stable and have a small amount of variation when subjected to external interference.
4) Compact structure, easy to install, debug, use, and maintain, and good versatility
Post time: Apr-03-2023