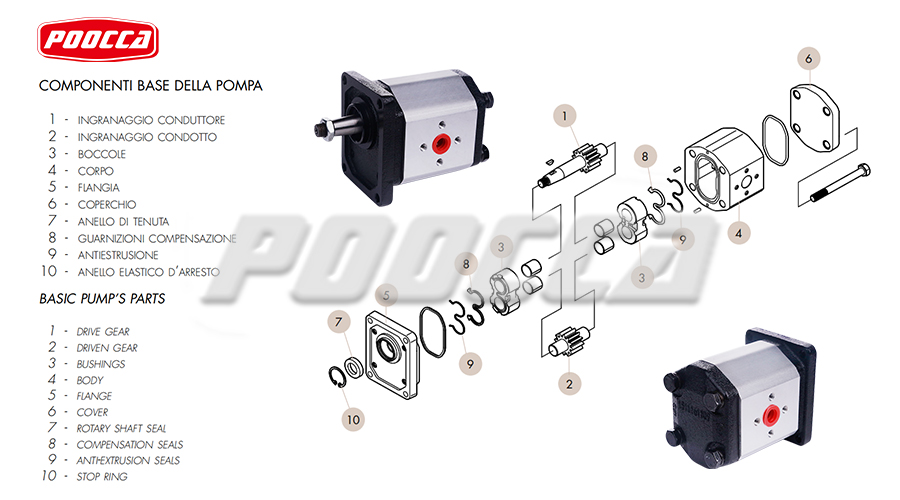
The continuous development of industrial equipment maintenance technology in this era has also put forward higher requirements for the repair technology of hydraulic gear pumps, a key component in the hydraulic system. As an important power transmission component, once the hydraulic gear pump fails, the efficiency of the entire hydraulic system will be affected.
Under long-term high-intensity working conditions, hydraulic gear pumps may experience various failures, such as reduced flow, unstable pressure, increased noise, etc. These failures are usually related to wear, contamination or changes in fit clearance within the pump. In order to solve these problems, maintenance personnel must have an in-depth understanding of the structure and working principle of hydraulic gear pumps and adopt appropriate gear pump maintenance strategies.
The first step in servicing a hydraulic gear pump is a thorough inspection and diagnosis. This includes inspecting the appearance of the pump to confirm whether there are signs of leakage or damage; listening to the sound of the pump when it is working to determine whether there are abnormal noises; and measuring the flow and pressure of the pump to ensure that they meet the working requirements. In addition, the hydraulic oil also needs to be tested, because contamination or deterioration of the oil is often one of the main causes of pump failure.
Step 1: Initial Assessment
Before diving into the repair process, it’s critical to perform a thorough evaluation of your hydraulic gear pump to identify the underlying problem. This includes inspecting pump components for leaks, unusual noises, reduced performance, or any obvious signs of damage. Additionally, checking fluid level and quality can provide valuable insights into the condition of the pump.
Step 2: Disassembly
Once the assessment is complete and the problem is identified, the next step is to carefully disassemble the hydraulic gear pump. Begin by disconnecting the pump from the hydraulic system and draining the hydraulic fluid to prevent spillage. Remove the mounting bolts and fittings holding the pump in place and carefully disassemble the pump components, noting the order and direction of reassembly.
Step 3: Inspect and Clean
After disassembling the pump, thoroughly inspect each component for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Pay close attention to gear teeth, bearings, seals, and housing surfaces. Replace any damaged or worn parts with genuine OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) replacement parts to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, clean all components with a suitable solvent to remove any contaminants or debris that may affect pump operation.
Step 4: Replace the seal
Seals play a key role in preventing fluid leakage and maintaining hydraulic pressure within the pump. Check seals for signs of wear, cracks or deformation as these can cause leaks and reduced pump efficiency. Replace all seals, including shaft seals, bearing seals and O-rings, with high-quality replacement parts that are compatible with the hydraulic fluid and operating conditions.
Step 5: Gear and Bearing Inspection
Gear assemblies and bearings are important components of hydraulic gear pumps, responsible for transmitting power and maintaining smooth operation. Check the gear teeth for signs of wear, pitting, or damage that could affect pump performance and efficiency. Likewise, check the bearings for excessive play, noise, or roughness that would indicate the need for replacement.
Step 6: Reassemble and test
After inspecting, cleaning, and replacing all parts as necessary, reassemble the hydraulic gear pump in the reverse order of disassembly. Ensure bolts, fittings and seals are properly aligned and tightened to prevent leaks and ensure optimal pump performance. After reassembly, the hydraulic system is refilled with the appropriate fluid and a series of tests are performed to verify the functionality of the pump, including pressure testing, flow measurements, and noise analysis.
Step 7: Preventive Maintenance and Monitoring
After repairing your hydraulic gear pump, implement a regular preventive maintenance program to ensure continued reliability and performance. This includes regular inspections, fluid analysis and proactive replacement of wear parts to prevent unplanned downtime and costly repairs. Additionally, monitor the operation of the pump closely for any signs of unusual behavior and resolve issues promptly to avoid further damage.
After the repair is completed, the hydraulic gear pump needs to be reassembled. During this process, it is very important to ensure that all parts are installed correctly and restored to their original positions. Also, replace all seals to prevent future leak problems. Once assembly is complete, it is essential to perform a test run of the system. This includes monitoring key pump parameters such as pressure, flow and temperature to ensure the pump is performing to design standards.
Finally, maintenance personnel should record all key steps and problems found during the maintenance process, which is very helpful for future maintenance and fault diagnosis. At the same time, regular maintenance and replacement of wearing parts can effectively extend the service life of the hydraulic gear pump.
In short, the maintenance of hydraulic gear pump is a highly professional and demanding job. Through accurate fault diagnosis, standardized disassembly procedures, meticulous cleaning work, strict assembly quality control and attention to details, the maintenance quality of the hydraulic gear pump can be ensured, thereby ensuring the stable operation of the entire hydraulic system.
Post time: Mar-27-2024